2. Causes of Abnormal Behavior
Risk Factors and Causes of Abnormal Behavior
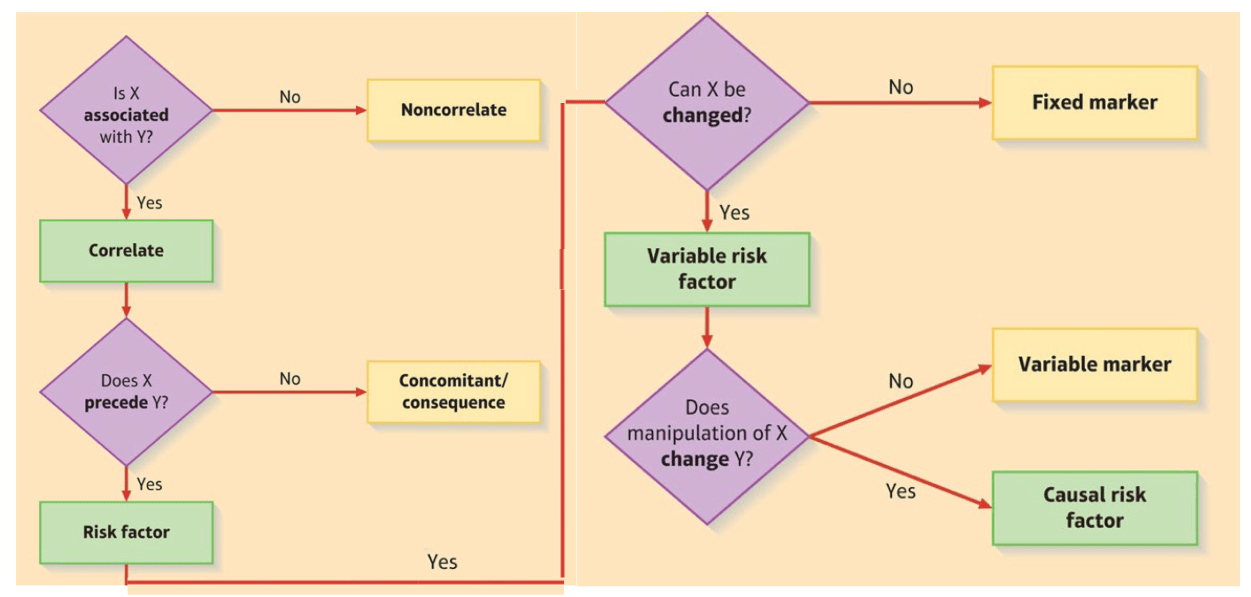
- A necessary cause (X) is a condition that must exist for a disorder (Y) to occur.
- A sufficient cause of a disorder is a condition that guarantees the occurrence of a disorder.
- A contributory cause is one that increases the probability of a disorder developing but is neither necessary nor sufficient for the disorder to occur.
Causes of Abnormal Behavior
- Distal risk factors are causal factors occurring relatively early in life that may not show their effects for many years.
- Proximal (immediate) risk factors are factors that operate shortly before the occurrence of the symptoms of a disorder.
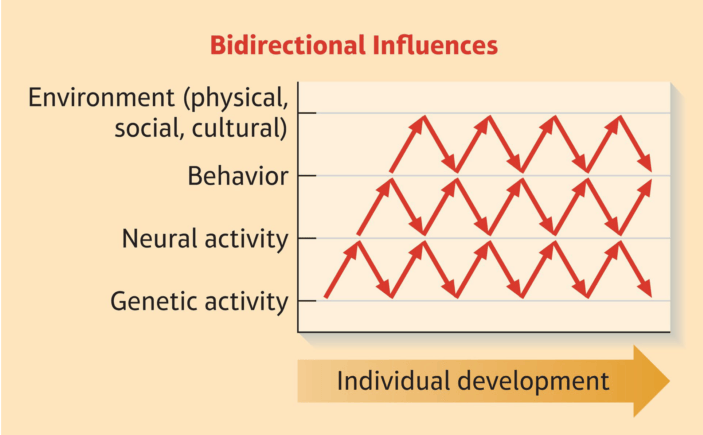
Feedback and Bidirectionality in Abnormal Behavior
In the study of abnormal psychology, it can be challenging to determine with certainty which conditions are causes and which are effects due to the complex and bidirectional nature of mental health disorders.
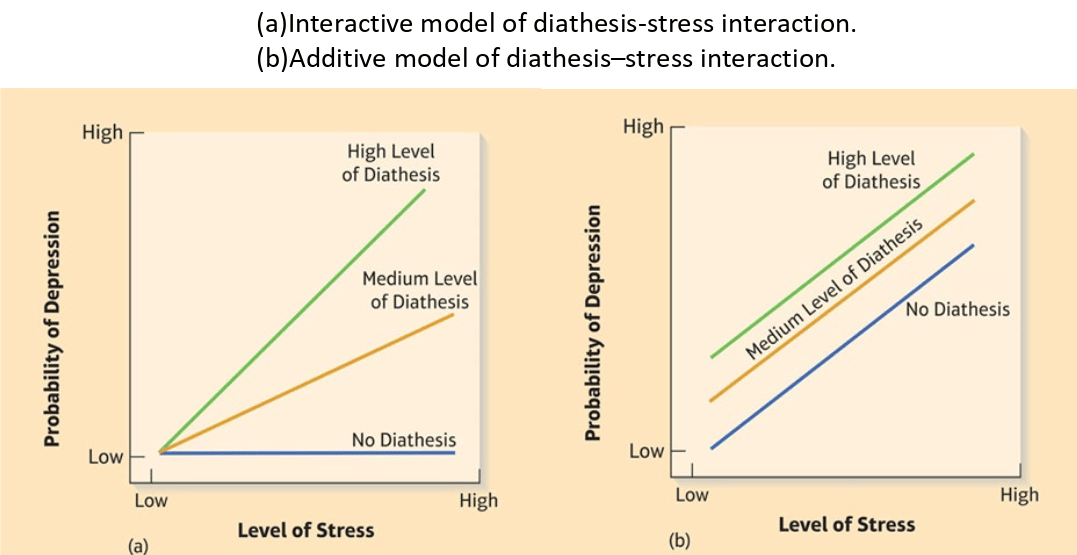
Diathesis-Stress Models
Combination of diathesis and stress to cause disorder.
- Diathesis: Relatively distal necessary or contributory cause that is not sufficient to cause disorder
- Stress: Response of individual to taxing demands.
Protective factors
Stronger Resilience with:
- Healthy Family environment
- Exposure to stressful experiences that are dealt with successfully
- Emotional intelligence
Perspectives to Understand the Causes of Abnormal Behavior
The Biological Perspective
Four categories of biological factors relevant to maladaptive behavior.
Genetic vulnerabilities
Heredity is important predisposing contributory cause for number of disorders.
The Relationship of Genotypes to Phenotypes
Genotype: Total genetic endowment.
Phenotype: Observed structural and functional characteristics.
Methods for Studying Genetic Influences
Traditional methods:
- Family history method
- Twin method
- Adoption method
More recent methods:
- Linkage analysis
- Association studies
Brain dysfunction and neural plasticity
Subtle deficiencies of brain function are rarely implicated in mental disorders.
Genetic programs for brain development are not as rigid and deterministic as was once believed.
The Developmental Systems Approach
Neuro-transmitter & hormonal abnormalities in brain and CNS
Neurotransmitter imbalances:
- Can result in abnormal behavior
- Created in various ways: overproduction, deactivation, abnormally sensitive or insensitive
5 Most studied neurotransmitter:
- Norepinephrine
- Dopamine
- Serotonin
- Glutamate
- Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA)
Hormonal Imbalances
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis:
- Messages (CRH) travel from the hypothalamus to the pituitary
- Pituitary releases ACTH, which stimulates cortical part of the adrenal gland, produces epinephrine (adrenaline) and cortisol
- Cortisol provides negative feedback to hypothalamus and pituitary to decrease their release of CRH and ACTH, which in turn reduces the release of adrenaline and cortisol
Temperament
Temperament:
Child’s reactivity and characteristic ways of self-regulation. Early temperament is basis from which personality develops.
Five Dimensions of Temperament:
- Fearfulness
- Irritability and frustration
- Positive affect
- Activity level
- Attentional persistence and effortful control
The Psychological Perspective
Psychodynamic
Freud theorized that a person’s behavior results from interaction of:
- Id (pleasure principle)
- Ego (reality principle)
- Superego (executive branch)
Newer Psychodynamic Perspectives:
- Ego psychology
- Attachment theory
- Object-relations theory
- Interpersonal perspective
Behavioral
- Classical Conditioning
- Operant Conditioning
- Generalization and Discrimination
- Observational Learning
Cognitive-Behavioral
- Schema: Underlying representation of knowledge that guides current processing of information
- Attributions: Process of assigning causes to things that happen
- Attributional style: Characteristic way in which individual may tend to assign causes to bad or good events
Cognitive Therapy:
- The way we interpret events and experiences determines our emotional reactions to them.
- Clinicians use a variety of techniques designed to alter a client’s negative cognitive biases.
The Social Perspective
Factors with detrimental effects on a child’s socioemotional development.
Early deprivation or trauma
- Depriving essential resources
- Institutionalization
- Neglect and abuse at home
- Separation from parents
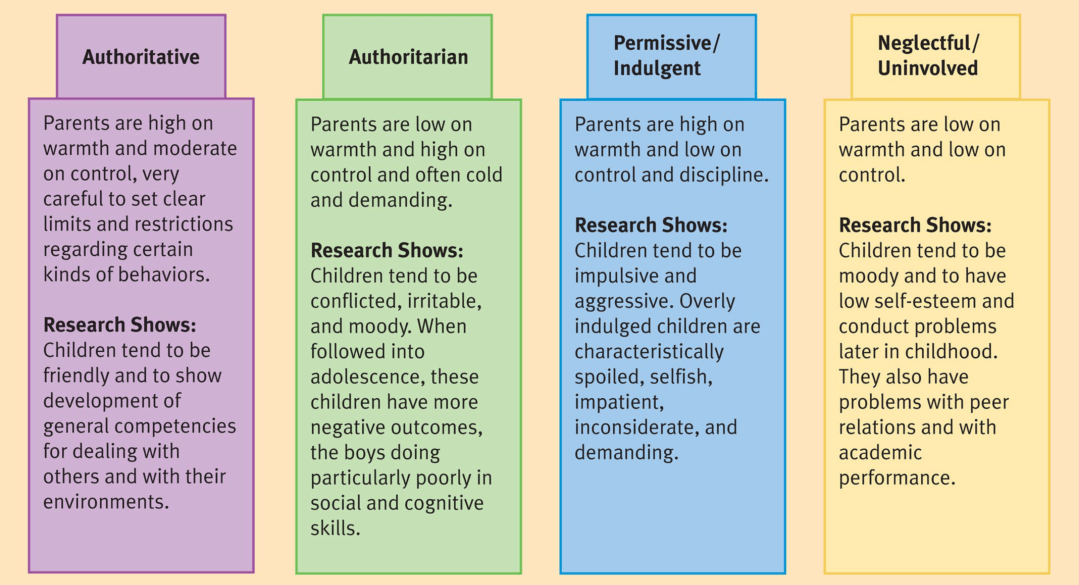
Problems in parenting style
A parent–child relationship is always bidirectional:
Parents who have various forms of psychopathology tend to have one or more children at heightened risk for a wide range of developmental difficulties.
Marital discord & divorce
Long-standing marital discord:
- Aggressive behavior
- Poor quality relationships
Divorce:
- Insecurity, rejection
- Delinquency
- Lower educational attainment
Low Socioeconomic Status and Unemployment
In our society, the lower the socioeconomic class, the higher the incidence of mental and physical disorders.
- Children and adolescents from lower socioeconomic status (SES) families tend to have more psychological problems.
- Studies have repeatedly found unemployment to be associated with enhanced vulnerability to psychopathology.
Maladaptive peer relation-ships
- Peer exclusion or abuse
- Proactive and reactive aggression in bullying
- Cyberbullying
Prejudice and Discrimination in Race, Gender, and Ethnicity
Increased prevalence of certain mental disorders may be related to:
- Prejudice against minority groups and women
- Perceived discrimination and self-esteem
The Cultural Perspective
Cultural context of behavior:
- Universal and Culture-Specific Symptoms of Disorders
- Culture: Over-and Undercontrolled Behavior
Universal and Culture-Specific Symptoms of Disorders
Universality of some disorders:
- Certain psychological symptoms are consistently found among similarly diagnosed clinical groups
Sociocultural factors:
- Which disorders develop
- Prevalence, course
Culture: Over- and Undercontrolled Problem
Undercontrolled problem:
- Agression, disobedience, disrespect
- Exhibited by American
Overcontrolled problem:
- Shyness, anxiety, depression
- Exhibited by Thai